Introduction
In today’s hyperconnected world, seamless and secure device communication has never been more essential. As industries accelerate toward AI-powered automation, smart workflows, and decentralized network models, one term keeps emerging in innovation circles: ZeroDeviceNet. Although still gaining traction, this new communication protocol architecture is increasingly considered a game-changer for scalable, autonomous networks in smart manufacturing, IoT ecosystems, and distributed control systems.
The growing demand for edge-ready infrastructure and self-sufficient node-based architecture requires more than traditional networking solutions. ZeroDeviceNet provides a unique framework prioritizing zero-configuration, peer-to-peer communication, and plug-and-play scalability all aligned with the future of machine-to-machine (M2M) interaction. This comprehensive guide explores what ZeroDeviceNet is, how it compares to legacy systems, and why it matters in a world shaped by real-time data and trusted responsiveness. Whether you’re an engineer, IT manager, or product developer, understanding this model could redefine how you build connected environments.
Understanding Device Communication Protocols
To understand why ZeroDeviceNet matters, it’s important to first break down how device communication has evolved. For decades, devices talked through centralized systems relying on a master-slave model, where a controller issued commands, and subordinate nodes responded.
These models include common frameworks such as
- Modbus
- CAN Bus
- DeviceNet
- Ethernet/IP
- OPC UA
While reliable, many older protocols struggled with flexibility, scalability, and compatibility in increasingly complex environments that demand interoperability across devices from varied vendors.
ZeroDeviceNet offers a shift by supporting autonomous, peer-aware, zero-configuration communication. It eliminates dependency on master devices by decentralizing control logic without sacrificing network coordination.
What Makes ZeroDeviceNet Different?
Unlike legacy systems that need central control units or extensive manual setup, ZeroDeviceNet thrives in environments that demand dynamic adaptability. Its name reflects its focus on zero configuration and device independence, providing automatic node recognition, negotiation, and communication.
Core Principles Include:
- Peer-to-peer communication rather than master/slave
- Zero configuration devices auto-discover and map themselves in real-time
- Protocol abstraction, meaning cross-compatibility across digital standards
- Blockchain-ready integration for immutable data logging
Because the protocol removes the need for control hubs, it’s gaining interest in edge computing infrastructures and Industry 4.0 platforms that demand fault tolerance and decentralized intelligence.
Real-World Applications in 2026
ZeroDeviceNet isn’t just theoretical; it’s already reshaping several industries by enhancing M2M coordination and reducing latency in automation processes.
Leading Use Cases:
- Smart manufacturing: Self-managing machines coordinate actions on production floors.
- IoT networks: Devices in homes and cities connect without central provisioning.
- Robotics: Autonomous bots share sensory data and task loads on the fly.
- Logistics: RFID tags and shipping monitors auto-adjust routes and schedules in real time.
In 2026, ZeroDeviceNet is being piloted in European smart city projects and Asian autonomous drone logistics systems, where security and responsiveness are critical.
Architecture of a ZeroDeviceNet System
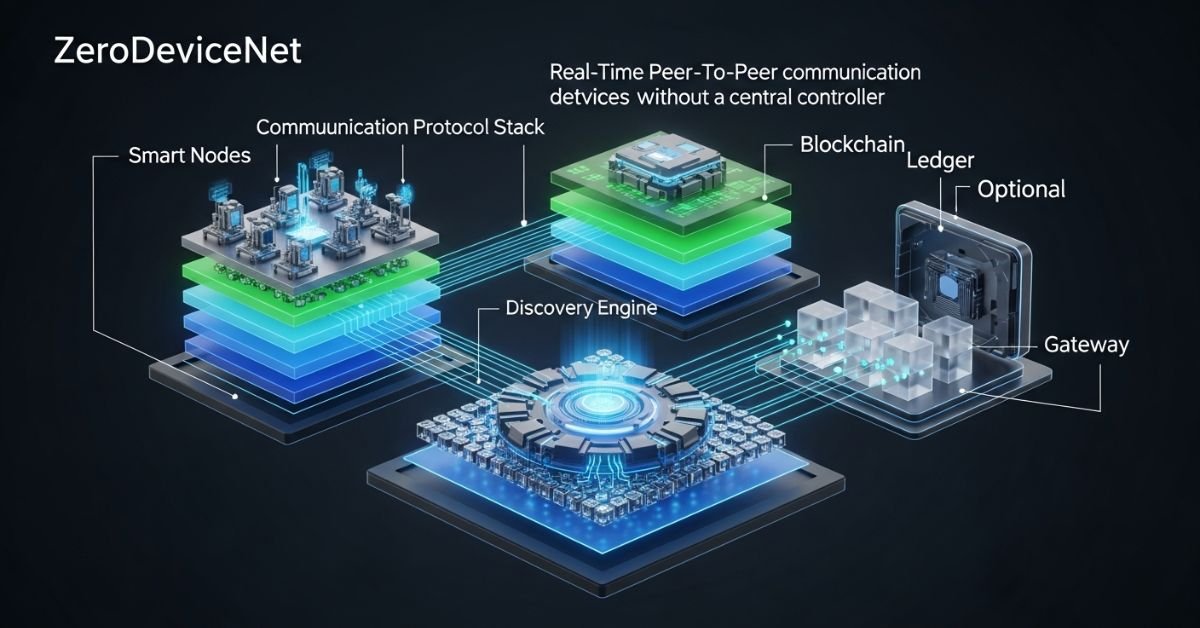
A ZeroDeviceNet system differs fundamentally from centralized bus networks. Instead of using a control unit to coordinate traffic, each node acts as both sender and receiver, using a shared protocol for initialization, communication, and acknowledgement.
Key Components:
- Smart nodes: Individual devices equipped with microcontrollers and compatible firmware.
- Discovery engine: Nodes identify each other upon connection dynamically.
- Communication protocol stack: Lightweight, cloud-compatible libraries.
- Security layer: Encryption + optional blockchain timestamping.
| Component | Function |
| Node Firmware | Handles messaging and discovery |
| Protocol Stack | Manages data formatting & routing |
| Gateway (optional) | Bridges to external IP networks |
| Ledger Integration | Adds verifiable system logs |
Decentralization doesn’t mean chaos, it means the absence of single failure points.
How It Integrates with IoT and Edge Systems
In edge networks, the time needed to send data to centralized servers for routing or analysis often introduces latency and risk. ZeroDeviceNet works at the edge, enabling devices to make transactional decisions instantly.
Integration Benefits:
- Faster sensor-triggered actions in industrial automation
- Reduced bandwidth usage since devices talk locally
- Enhanced security due to limited external exposure
- Lower installation and maintenance overheads
Smart grids, autonomous agriculture equipment, and wearable health tech now increasingly require this model. It aligns perfectly with the ongoing trend of reducing cloud dependency without compromising data autonomy.
Benefits Over Traditional Network Topologies
Legacy networks are structured in hierarchical layers: applications, logic, transport, and physical connectivity. But these levels often introduce complexity and increase the risk of bottlenecks.
ZeroDeviceNet Advantages:
- No central point of failure
- Auto-configuring nodes reduce deployment time.
- Self-healing capabilities
- Backward compatible interface modules available
| Feature | Traditional Protocols | ZeroDeviceNet |
| Deployment Time | High | Low |
| Security Risk | Central weak points | Distributed |
| Reconfiguration Flexibility | Manual | Automatic |
| Maintenance Cost | Medium to High | Low |
With lower total cost of ownership (TCO), ZeroDeviceNet is making inroads into lean businesses and mid-tier manufacturers looking for agility without IT overhead.
Challenges and Limitations
No protocol is without hurdles, and ZeroDeviceNet has a few of its own especially in large-scale deployments.
Current Challenges:
- Adoption barriers due to limited vendor support
- Incompatibility with legacy infrastructure
- Standardization is still evolving, making certification harder.
- Skills gap in zero-config node programming
Without a large standards body backing its development yet, companies must rely on internal or vendor-supported adaptation. However, foundations like the Open Automation Forum (OAF) are exploring broader standardization paths for decentralized device protocols.
Comparison with Popular Protocols in 2026
| Protocol | Configuration Needed | Central Controller | Edge Ready | Blockchain Support |
| Modbus | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| DeviceNet | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| OPC UA | Medium | Optional | Partial | Experimental |
| ZeroDeviceNet | No | No | Yes | Yes |
This comparison highlights why newer systems are leaning toward lightweight, decentralized frameworks that reduce complexity and boost adaptability.
Security Enhancements Through Decentralization
Cybersecurity is a growing pain point in automation. The use of decentralized protocols can minimize some risks especially from DDoS attacks or single-point breaches.
Security Advantages:
- Device-to-device encryption with individual keys
- Minimal exposure to centralized APIs
- Built-in redundancy reduces network vulnerability.
- Optional immutable data capture using distributed ledgers
These features fulfill core principles of least privilege and zero trust, making ZeroDeviceNet a strong architectural layer for security-first deployments in sensitive sectors like defense or healthcare.
What’s Next: The Future of ZeroDeviceNet
As adoption grows, analysts believe that ZeroDeviceNet (or its derivative open protocol models) could underpin the next generation of industrial and consumer-grade device interaction.
Predictions for 2026–2028:
- Wider adoption in autonomous vehicle systems
- Open-source community versions powering retrofitting kits
- Integration into AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) stacks
- Certification standards released by global tech consortiums
The goal is not just zero configuration but zero friction—networking simplified to the point where devices engage as naturally as users do on social media. When every object in a system can think, communicate, and evolve without human intervention, the limits of automation shift radically forward.
FAQs
What is ZeroDeviceNet?
A decentralized, plug-and-play device communication protocol prioritizing real-time edge networking.
Is ZeroDeviceNet compatible with existing Modbus systems?
No, it uses a fundamentally different peer-based architecture but can be bridged via custom gateways.
Does it require the internet to function?
No, it works in completely offline environments by enabling localized device-to-device communication.
Is it open-source?
As of 2026, community and private deployments exist; an open-standard version is under development.
Can ZeroDeviceNet be used in consumer-grade products?
Yes, including smart appliances and robotics; however, enterprise adoption remains more widespread currently.
Conclusion
ZeroDeviceNet represents a substantial leap forward in how machines connect, synchronize, and evolve in an increasingly digital and decentralized world. By eliminating the complexities of traditional network hierarchies and empowering devices to communicate directly, it opens doors for scalable automation, edge intelligence, and self-managing systems.
Industries that embrace this protocol position themselves not just for better efficiency but also for futureproofing against the inevitable rise of connected autonomy. If your systems still rely heavily on centralized logic, now may be the time to explore what ZeroDeviceNet or similar architectures can offer.
Next Step: Evaluate your existing infrastructure and identify areas where decentralized networking could improve resilience, reduce latency, or automate operations. Consider a pilot implementation with vendor-supported ZeroDeviceNet-ready devices to get started.




